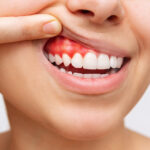
Bleeding gums treatment is crucial if you experience bleeding gums while brushing. You’re not alone. This common dental issue can be a sign of an underlying problem and shouldn’t be ignored. While occasional bleeding might seem minor, it can be a symptom of gum disease, a serious condition that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. This comprehensive guide will delve into the root causes of bleeding gums, explore effective treatment options, and provide valuable prevention tips. By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of how to maintain healthy gums and a radiant smile.
Causes of Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums, medically known as gingival bleeding, can stem from various factors:
- Gingivitis: This is the earliest stage of gum disease, characterized by inflammation of the gum tissues. Poor oral hygiene, allowing plaque (a sticky film of bacteria) to build up around the gum line, is the primary culprit.
- Periodontal Disease: A more advanced stage of gum disease where the infection spreads beyond the gums and affects the underlying bone supporting the teeth. This can lead to loose teeth, bone loss, and even tooth loss.
- Injury: Trauma to the gums, such as from vigorous brushing, accidental biting, or dental procedures, can cause temporary bleeding.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels during pregnancy or puberty can increase gum sensitivity and bleeding.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, including blood thinners and anticoagulants, can make it easier for gums to bleed.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamin C and vitamin K can weaken blood vessels and increase the risk of bleeding.
- Smoking: Smoking weakens the immune system and reduces blood flow to the gums, making them more susceptible to infection.
Recognizing the Signs of Gum Disease
Early detection is key to effective treatment. Besides bleeding gums, watch out for these warning signs:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bad breath that persists
- Receding gums (gums pulling away from the teeth)
- Loose teeth
- Pus formation around the teeth
- Pain while chewing
Bleeding gums treatment
The treatment approach will depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition:
- Improved Oral Hygiene: This is the cornerstone of treatment. Brush your teeth twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush and floss once a day. Consider using an antibacterial mouthwash as recommended by your dentist.
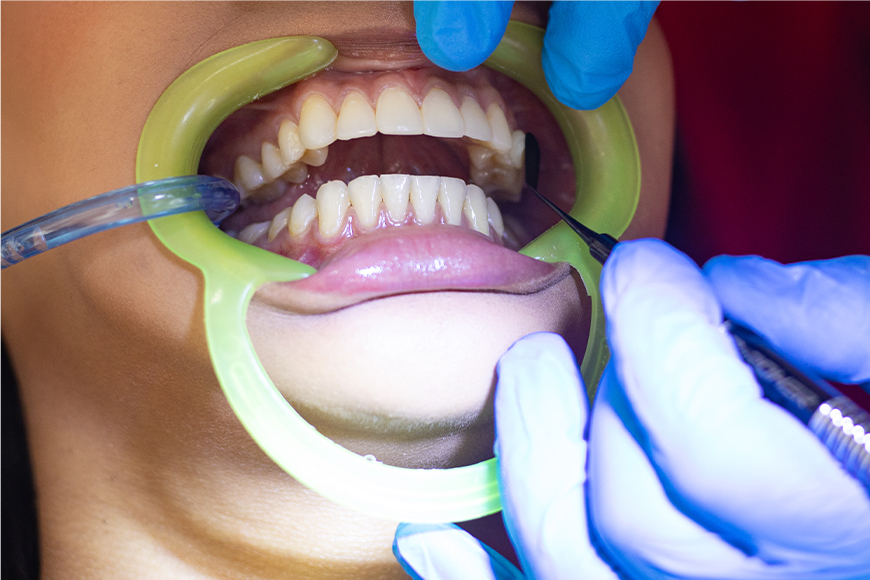
- Professional Cleaning: Regular dental checkups and professional cleanings are crucial. Your dentist will remove plaque and tartar buildup that you can’t reach at home.
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line.
- Medications: In some cases, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics or antiseptics to combat infection.
- Surgical Procedures: For severe cases of periodontal disease, surgical procedures may be necessary to reduce gum pockets, regenerate bone, or improve tissue attachment.
Home Remedies for Soothing Bleeding Gums
While home remedies can offer temporary relief, they should not replace professional dental care. Here are a few options:
- Salt Water Rinse: Mix a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and gently rinse your mouth several times a day.
- Hydrogen Peroxide Rinse: Dilute hydrogen peroxide with water and use it as a mouthwash. However, use it sparingly as it can irritate the gums.
- Tea Tree Oil Rinse: Add a few drops of tea tree oil to water and rinse your mouth gently.
Preventing Bleeding Gums
The best way to prevent bleeding gums is to practice excellent oral hygiene:
- Brush twice daily: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle circular motions.
- Floss daily: Flossing removes plaque from between your teeth where your toothbrush can’t reach.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash: As directed by your dentist.
- Quit smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of gum disease.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and calcium-rich foods in your diet.
- Schedule regular dental checkups: Visit your dentist for professional cleanings and examinations at least twice a year.
When to See a Dentist
If you experience persistent bleeding gums, even after improving your oral hygiene, schedule an appointment with your dentist. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent the progression of gum disease and save your teeth.
Madison Dentistry & Implant Center: Your Trusted Dental Partner
At Madison Dentistry & Implant Center, we are committed to providing comprehensive and personalized dental care to patients in Madison and the surrounding communities of Morristown, Chatham, Florham Park, and Harding. Our experienced team of dentists utilizes the latest techniques and technology to diagnose and treat gum disease effectively. We offer a wide range of services, including:
- Comprehensive dental exams and cleanings
- Gum disease treatment
- Periodontal surgery
- Dental implants
- Cosmetic dentistry
We believe in building long-term relationships with our patients and providing exceptional care in a comfortable and welcoming environment.
Conclusion
Bleeding gums can be a warning sign of underlying oral health issues. By understanding the causes and implementing preventive measures, you can maintain healthy gums and a beautiful smile. Remember to practice excellent oral hygiene, schedule regular dental checkups, and consult with your dentist if you have any concerns. Schedule your consultation with us today!